LLM Analytics — Paving the way to Production for LLM Apps
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
LLM Analytics - Paving the way to Production for LLM Apps
Enterprising Challenge with LLMs
Large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly popular recently, with applications ranging from generating text and translating languages to writing creative content and answering questions in an informative way or even doing some actions with some agents and tools. However, LLMs can also be complex and difficult to use, especially in production environments, it is kind of black box to customers.
LLM Analytics is a key feature of building and deploying LLM applications in production. It is the ability to monitor and understand the performance and behavior of LLMs in real time. This can help to identify and resolve issues quickly, and to ensure that LLMs are meeting the needs of their customers. Basically, the LLM Analytics should be evaluated from the following five core pillars:
- Debugging
- Testing
- Evaluation
- Tracing
- Usage Metris
Five Core Pillars for LLM Analytics
Debugging
-
Debugging is the process of identifying and fixing errors in software. LLMs can be difficult to debug because they are complex systems with many interconnected parts. However, there are a number of tools and techniques that can be used to debug LLMs.
-
One common approach is to use logging and telemetry data to track the execution of the LLM. This data can be used to identify areas of the LLM that are not working as expected. Another approach is to use symbolic execution to explore all possible paths through the LLM and identify potential errors.
Testing
-
Testing is the process of evaluating the performance and correctness of software. LLM testing can be challenging because LLMs are trained on large datasets, and it can be difficult to generate test cases that cover all possible inputs and outputs.
-
However, there are a number of techniques that can be used to test LLMs. One common approach is to use unit testing to test individual components of the LLM. Another approach is to use integration testing to test how the different components of the LLM work together. Finally, system testing can be used to test the LLM as a whole.
Evaluation
- Evaluation is the process of assessing the quality of an LLM. LLM evaluation can be challenging because there is no single metric that can be used to measure the quality of an LLM.
- Different LLMs use different algorithms, different training data, different weighting on data, and different pre and post processing.
- The quality of the answers will rely on picking the correct LLM for the problem domain.
- One common approach to LLM evaluation is to use human judges to rate the quality of the outputs produced by the LLM. Another approach is to use automatic evaluation metrics, such as BLEU and ROUGE.
Tracing
- Tracing is the process of tracking the execution of an LLM. This can be useful for debugging and optimizing LLMs.
- It can help us track the answer back to the original documents to make sure the model answer questions based on facts and not making it up (“hallucinating”).
- There are a number of different tracing frameworks that can be used to trace LLMs, such as TensorFlow Debugger and PyTorch Profiler.
Usage metrics
- Usage metrics are metrics that track how an LLM is used. This information can be used to improve the performance and usability of the LLM.
- Some common usage metrics include the number of requests per second, the average time spent using the LLM, and the most popular LLM tasks.
- Sometimes we can also compare the metrics with different models and select the best model for some scenarios.
Projects for LLM Analytics
LangSmith
LangSmith is a platform for building production-grade LLM applications.
It lets you debug, test, evaluate, and monitor chains and intelligent agents built on any LLM framework and seamlessly integrates with LangChain, the go-to open source framework for building with LLMs.
LangSmith is currently in private beta, I’m also not sure if it has any plan to open source in future.
LangFuse
Langfuse is an open source product analytics suite for LLM apps. It is mostly geared towards production usage but some users also use it for local development of their LLM applications.
It provides kind of Observability and Analytics features. For Observability, it can help on Nested view of LLM app executions; detailed information along the traces on: latency, cost, scores; It can also help you trace the segment execution so as to identify the root cause of the issue. For Analytics, it can help to report some metrics such as token usage, model comparison, model latency etc.
You can either deploy LangFuse locally or use a public service at https://langfuse.com/
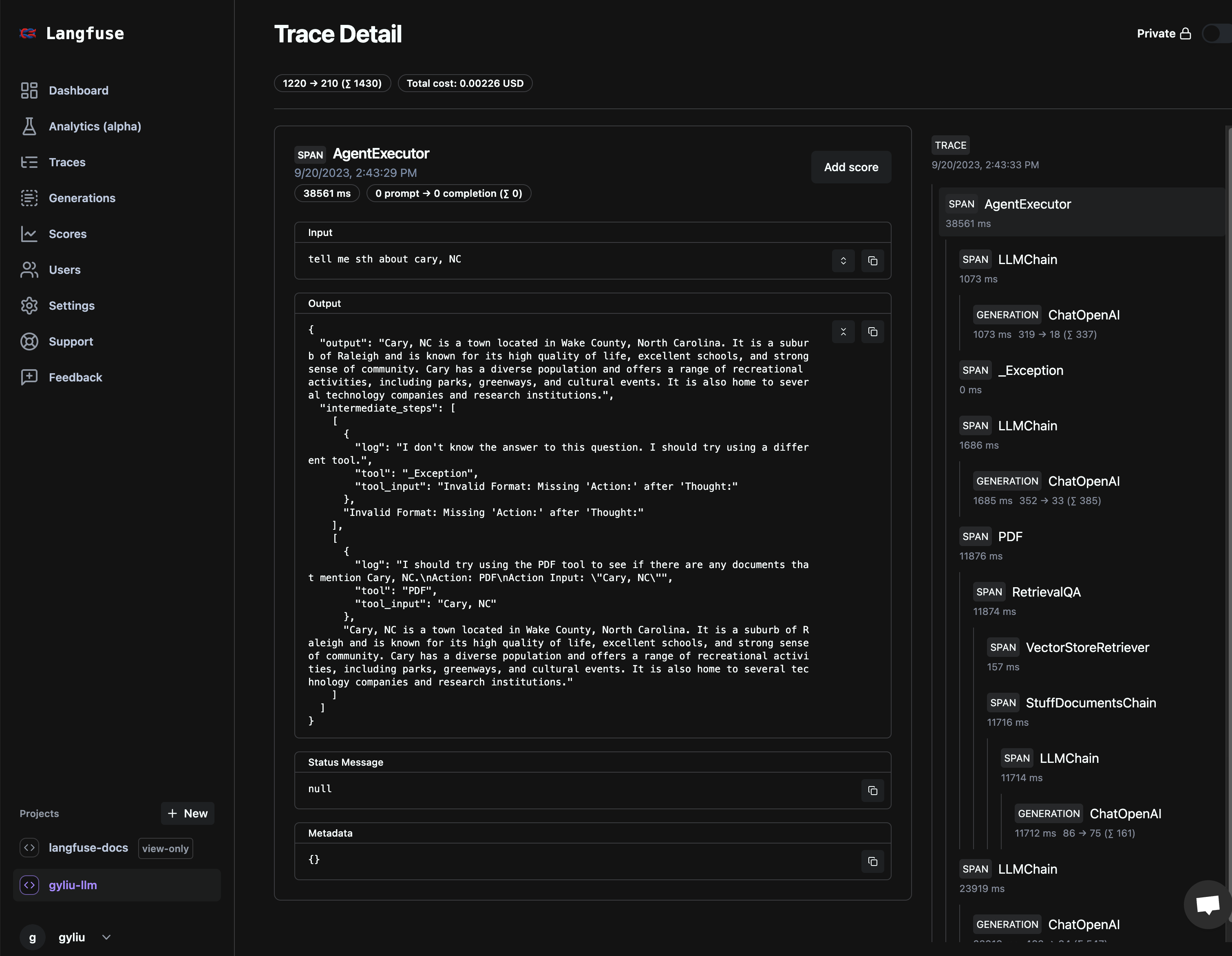
The following is a snapshot of how LangFuse tarcing works with a LLM chain. LangFuse has been integrated to LangFlow now, you can refer to Integrating Langfuse with Langflow for detail.
Conclusion
It seems the tool chain for building LLM Apps are evolving fast. Now we can probably say LangChain, LangFlow, Flowise etc are tools which are used for LLM Apps prototyping; LangSmith, LangFuse etc are tools which are used from LLM Apps move to production, we can use those tools to build a full pipeline to build LLM Apps.