The Future of AI-Driven Products: UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
- The Future of AI-Driven Products: UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data
The Future of AI-Driven Products: UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data
Introduction
The rise of AI-powered applications is reshaping how businesses interact with their customers and data. The future of AI related products is no longer just about automation, it’s about adaptive, real-time decision-making powered by AI agents.
A new paradigm is emerging where UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data forms the foundation of next-generation applications. This architecture enables systems to not only understand user requests but also reason, take actions, and automate workflows based on real-time customer data.
In this blog, we’ll explore how LLM agents enhance traditional AI-powered products, making them more autonomous, interactive, and intelligent.
The New AI Product Architecture: UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data
Traditional applications require manual input and predefined workflows, but the future is shifting towards AI-driven agents that can act independently based on user intent and customer data.
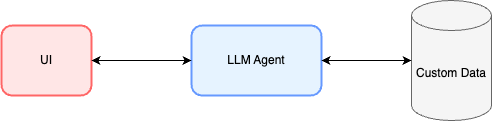
Here’s how these three key components work together:
- UI
- The primary interaction layer (chatbot, dashboard, voice assistant, API, etc.).
- Users run commands or ask natural language questions via the UI interaction.
- The UI serves as a gateway for the user to interact with the LLM agent.
- LLM Agent
- Unlike basic LLM chatbots, an LLM Agent can reason, plan, and execute tasks.
- It translates user intent into structured queries and actions.
- The agent calls APIs, retrieves customer data, and takes actions autonomously based on business logic.
- Customer Data (Databases, APIs, Logs, etc.)
- The source of truth that the LLM Agent operates on.
- Can be structured (PostgreSQL, MongoDB) or unstructured (emails, tickets, logs).
- The LLM Agent must have secure, permission-aware access to this data.
This setup allows AI-powered applications to go beyond just answering questions—they can now understand context, analyze patterns, and automate actions.
How UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data Work Together
User Requests Information or Action via the UI
- The UI could be a chatbot, an enterprise dashboard, or a voice assistant.
- The user can ask in natural language:
- “Summarize the latest customer complaints and suggest follow-up actions.”
- “Find all overdue invoices and notify the finance team.”
LLM Agent Interprets and Plans the Task
- The LLM agent understands the user’s intent and business rules.
- It generates a plan:
- Calls APIs or queries databases for relevant information.
- Uses tools like SQL generators or vector search for retrieval.
- Determines if an action needs to be taken.
Querying Customer Data
- The system retrieves real-time customer data from databases, CRMs, or logs.
- The LLM agent analyzes patterns (e.g., customer sentiment, financial trends).
Intelligent Decision & Action Execution
- Instead of just returning raw data, the LLM Agent suggests or takes actions:
- Escalates critical support tickets.
- Automates sending reports to relevant teams.
- Flags fraudulent transactions for review.
- Recommends personalized follow-ups based on past interactions.
User Receives an Actionable Response
- The UI presents insights, summaries, or action buttons for user confirmation.
- In fully automated workflows, the AI agent can execute the task autonomously.
This end-to-end automation transforms AI from a passive chatbot into a proactive AI copilot that assists users in real time.
Key Use Cases of UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data
AI-Powered Business Intelligence
- Enhanced Data Querying: Users can interact with the system in natural language without needing to know SQL or complex query languages. The LLM Agent interprets the query, translates it into an optimized data request, and then retrieves insights from structured and unstructured data sources.
- Advanced Trend Analysis: Beyond simple reporting, the agent can analyze historical data to detect seasonal patterns, emerging trends, or anomalies that may indicate underlying issues or opportunities. This includes forecasting, predictive analytics, and scenario planning.
- Actionable Insights: Once the analysis is complete, the system not only presents visualizations and reports but also suggests actionable strategies. For example, after querying revenue growth over the past six months, the agent might propose targeted marketing campaigns or resource reallocation based on forecasted sales.
- Example Use Case: “Show revenue growth for the last 6 months, generate a detailed sales forecast, and recommend strategies to boost revenue during upcoming slow periods.”
AI Copilots for Enterprise Teams
- Cross-Departmental Support: LLM Agents serve as intelligent assistants for various teams—finance, HR, IT, security, and more—by aggregating data from multiple sources and offering real-time analysis tailored to departmental needs.
- Automated Routine Tasks: The agent can automate repetitive tasks such as compliance monitoring, payroll reviews, or system health checks. For instance, by monitoring employee training records, it can identify gaps and trigger automatic reminders or scheduling for compliance sessions.
- Real-Time Collaboration: These agents facilitate real-time collaboration by integrating with enterprise communication tools, allowing teams to share insights and updates instantaneously. They help in decision-making during meetings by pulling up relevant data on demand.
- Example Use Case: “Identify all employees who have not completed compliance training, generate a summary report for the HR department, and automatically send reminders with scheduled training options.”
AI-Powered Customer Support
- Comprehensive Customer Insights: The LLM Agent can access and synthesize customer history from various touchpoints—including previous support tickets, emails, and feedback—providing a holistic view of each customer’s journey.
- Sentiment Analysis and Prioritization: By leveraging natural language processing, the system can assess the sentiment of customer communications and prioritize tickets based on urgency, customer value, or historical context.
- Proactive Recommendations: Rather than simply summarizing data, the agent can recommend tailored responses, propose retention strategies, or even initiate proactive outreach to resolve recurring issues before they escalate.
- Example Use Case: “Summarize past complaints from Customer X, identify recurring issues, and suggest a personalized retention strategy that includes automated follow-up messages and special offers.”
AI-Driven E-commerce & Personalization
- Behavioral Analysis: The system can analyze browsing history, purchase patterns, and demographic data to understand customer behavior at a granular level. This analysis allows businesses to predict future buying patterns and identify potential churn risks.
- Dynamic Personalization: Using real-time data, the agent can deliver personalized recommendations, offers, or discounts tailored to individual customer preferences. This includes adjusting website content dynamically or sending personalized email campaigns.
- Integrated Marketing Strategies: The agent can work alongside CRM and marketing automation platforms to optimize cross-channel marketing efforts, ensuring consistency and relevancy in messaging across platforms.
- Example Use Case: “Identify VIP customers who haven’t made a purchase recently, analyze their historical buying behavior, and send them a custom discount along with personalized product recommendations.”
AI-Augmented IT & DevOps Automation
- Anomaly Detection and Incident Response: AI agents monitor system logs, performance metrics, and security alerts in real time to identify anomalies. Once a potential issue is detected, they can either alert IT teams or automatically execute predefined remediation steps.
- Automated System Optimization: By continuously analyzing performance data, the agent can suggest and implement optimizations such as load balancing, resource allocation adjustments, or code-level tweaks to improve system stability and performance.
- Integration with DevOps Tools: The LLM Agent can interface with tools like Kubernetes, Jenkins, or other CI/CD pipelines, providing insights into deployment issues, automating rollbacks, or scheduling maintenance tasks based on predictive failure models.
- Example Use Case: “Analyze system logs to identify trends in high CPU usage, diagnose potential root causes, and propose fixes or schedule automated maintenance routines to prevent future incidents.”
Why LLM Agents Are the Future of AI-Driven Products
Moving Beyond Simple Chatbots
- From Reactive to Proactive: Traditional chatbots are largely reactive, handling predefined queries with scripted responses. LLM Agents, however, are designed to understand complex contexts and proactively drive workflows.
- Integrated Reasoning Capabilities: They can integrate reasoning capabilities that allow them to not only respond but also to predict user needs and initiate follow-up actions based on previous interactions.
- Expanding Functionality: This transformation means that rather than merely providing information, these agents can complete transactions, trigger business processes, and seamlessly integrate with broader enterprise systems.
Smarter, Context-Aware Interactions
- Personalized Engagement: LLM Agents continuously learn from interactions and adjust their responses based on user preferences, historical data, and real-time context. This leads to highly personalized experiences.
- Adaptive Learning: They can recall past interactions, understand context over extended conversations, and dynamically adjust to new information. For instance, if a user consistently checks customer churn data, the agent can autonomously generate weekly reports tailored to that metric.
- Enhanced Accuracy: With fine-tuning and feedback loops, these agents improve over time, reducing errors and ensuring that the context of interactions is accurately maintained.
Task Automation & Decision-Making
- End-to-End Automation: LLM Agents do more than just provide answers—they can execute a series of tasks. This includes generating alerts, updating records, scheduling activities, and even directly interfacing with other software systems to complete multi-step workflows.
- Decision Support: By synthesizing vast amounts of data and aligning it with business rules, the agents can support or even make decisions autonomously. This is particularly valuable in time-sensitive environments such as financial trading, emergency response, or IT incident management.
- Scalability: Automation driven by LLM Agents can scale across large datasets and diverse business functions, significantly reducing manual intervention and streamlining operations.
Integration with Business Logic
- Seamless Workflow Integration: LLM Agents are designed to operate within the context of existing business systems. By integrating with enterprise software, CRMs, and ERP systems, they ensure that all actions comply with established business logic and regulatory requirements.
- Custom Fine-Tuning: Through continuous training on domain-specific data, these agents can be customized to reflect an organization’s unique policies, compliance mandates, and operational nuances.
- Regulatory Compliance: With built-in checks and balances, the agents can enforce business rules and maintain consistency across all automated actions, ensuring that every decision aligns with corporate standards and legal requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Security & Access Control
- Robust Security Frameworks: Ensuring that AI Agents only access authorized data is paramount. This involves implementing robust security measures such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), data masking, and strict query guardrails.
- Privacy Compliance: Organizations must comply with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) by ensuring that customer data is handled securely and that any automated access does not expose sensitive information.
- Auditability: Maintain comprehensive logs and audit trails for all data accessed and actions taken by the LLM Agents, ensuring accountability and traceability in automated processes.
LLM Accuracy & Business Logic Compliance
- Domain-Specific Training: To minimize errors and “hallucinations,” it is crucial to fine-tune LLMs using domain-specific data. This ensures that the agents are well-versed in industry jargon, specific business processes, and unique customer interactions.
- Ongoing Validation: Continuous monitoring and validation processes should be established to regularly assess the accuracy of the LLM’s outputs and its adherence to business logic.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement robust feedback loops where users can report inaccuracies or provide suggestions, allowing the model to improve over time.
Query Optimization & Performance
- Handling Large Datasets: Large and complex datasets require optimized query strategies. Techniques such as query caching, indexing, and using hybrid models (e.g., vector databases for high-dimensional data) can significantly improve performance.
- Balancing Speed and Accuracy: While it is important to retrieve data quickly, maintaining high accuracy in analysis is equally critical. Employing advanced algorithms that balance these needs is essential.
- Scalable Infrastructure: Ensure that the underlying infrastructure can scale efficiently with increasing data loads and query demands, incorporating both on-premise and cloud-based solutions as needed.
Cost & Infrastructure Considerations
- Efficient Inference Strategies: Running AI agents at scale necessitates strategies that optimize LLM inference, such as on-demand model execution and cloud-based inference optimizations.
- Resource Allocation: Evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of deploying these advanced systems. The infrastructure should support scalable model deployments without incurring prohibitive costs.
- Investment in Technology: Continuous investment in both hardware (e.g., GPUs, TPUs) and software improvements is necessary to keep pace with evolving model architectures and to ensure sustained performance improvements over time.
Conclusion
The future of AI-driven applications is UI + LLM Agent + Customer Data. Unlike traditional static dashboards and rule-based automation, AI-powered agents provide real-time, context-aware decision-making and workflow automation.
By implementing this architecture, businesses can create autonomous, intelligent AI copilots that enhance productivity, improve customer engagement, and unlock new levels of efficiency.
Simple is the best, right?