Build and Run a Go MCP Server in 5Mins
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
Build and Run a Go MCP Server in 5Mins
In this tutorial, I will go through the end to end flow to build a MCP Go Server in 5Mins. This Go MCP Server will leverage MCP Go Library from mark3labs.
Benefit of Using Go for MCP Server
Using Go (Golang) to build a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server makes a lot of sense for several practical and architectural reasons. Here’s a breakdown of why Go is a strong choice for building a protocol server like MCP:
- Performance with Concurrency
- Go was designed for building high-performance network services.
- Its goroutines (lightweight threads) and channel-based concurrency make it easy to handle many simultaneous connections with low overhead.
- This is perfect for a protocol server that needs to serve multiple model context requests in parallel.
- Ease of Building and Deployment
- Go compiles into a single static binary, making deployment and distribution extremely easy—especially for microservices or edge deployments.
- Great for containerized environments like Kubernetes.
- Ecosystem and Tooling
- Tools like buf (for protobuf management), cobra (for CLI), viper (for config), and zap or logrus (for logging) are well-supported in Go.
- Makes it easy to build a production-ready MCP server quickly.
- Cloud Native Compatibility
- Go is a first-class citizen in the Cloud Native ecosystem (Kubernetes, Prometheus, Istio, etc.).
- If your MCP server will run in a Kubernetes environment or needs to expose metrics for observability, Go makes integration simple.
Pre-Reqs
Go installed. For my environemnt, I was using go 1.23
# go version
go version go1.23.4 darwin/arm64
Build the MCP Server
Init GO MCP Server
My GOPATH is /Users/gyliu513/go/src/github.com/gyliu513, so now I will create a folder to host this demo project under this GOPATH named as mcp-go-server.
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro ~ % mkdir mcp-go-server
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro ~ % cd mcp-go-server
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server %
Init your mcp go server project.
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server % go mod init
go: creating new go.mod: module github.com/gyliu513/mcp-go-server
Install mcp-go library.
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server % go get github.com/mark3labs/mcp-go
go: added github.com/mark3labs/mcp-go v0.18.0
Create the Go MCP Server
For this example, I was copying an example from mcp go examaple. This Go file implements a basic calculator tool server using the MCP (Model Context Protocol) framework.
The tool name is calculate, and this tool support add, subtract, multiply and divide.
The content of this file is as below, I will save it as mcp-go-server.go under this directory.
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/mark3labs/mcp-go/mcp"
"github.com/mark3labs/mcp-go/server"
)
func main() {
// Create a new MCP server
s := server.NewMCPServer(
"Calculator Demo",
"1.0.0",
server.WithResourceCapabilities(true, true),
server.WithLogging(),
)
// Add a calculator tool
calculatorTool := mcp.NewTool("calculate",
mcp.WithDescription("Perform basic arithmetic operations"),
mcp.WithString("operation",
mcp.Required(),
mcp.Description("The operation to perform (add, subtract, multiply, divide)"),
mcp.Enum("add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"),
),
mcp.WithNumber("x",
mcp.Required(),
mcp.Description("First number"),
),
mcp.WithNumber("y",
mcp.Required(),
mcp.Description("Second number"),
),
)
// Add the calculator handler
s.AddTool(calculatorTool, func(ctx context.Context, request mcp.CallToolRequest) (*mcp.CallToolResult, error) {
op := request.Params.Arguments["operation"].(string)
x := request.Params.Arguments["x"].(float64)
y := request.Params.Arguments["y"].(float64)
var result float64
switch op {
case "add":
result = x + y
case "subtract":
result = x - y
case "multiply":
result = x * y
case "divide":
if y == 0 {
return nil, errors.New("Cannot divide by zero")
}
result = x / y
}
return mcp.NewToolResultText(fmt.Sprintf("%.2f", result)), nil
})
// Start the server
if err := server.ServeStdio(s); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Server error: %v\n", err)
}
}
After the new file created, run go mod tidy to update dependency.
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server % go mod tidy
Build the Go MCP Server
Run go build to build this Go MCP Server. After the command finished, you will see the new Go MCP Server Binary named as mcp-go-server has been generated.
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server % go build
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server % ls
go.mod go.sum mcp-go-server mcp-go-server.go
Please note this binary is located at /Users/gyliu513/go/src/github.com/gyliu513/mcp-go-server, we will config this path to enable MCP Host can connect to this server.
gyliu513@Guangyas-MacBook-Pro mcp-go-server % pwd
/Users/gyliu513/go/src/github.com/gyliu513/mcp-go-server
Run the Go MCP Server
Now, we can run this Go MCP Server. For my case, I was using Claude to run and interact with this Go MCP Server. You can check my previous blog MCP Developer Quick Start to see how to config and run Claude Desktop.
Config claude_desktop_config.json
I was using MacOS, and this file is located at ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json. Add the followinng content to this file to enable Claude Desktop can connect to the Go MCP Server that we created.
{
"mcpServers": {
"go-server": {
"command": "/Users/gyliu513/go/src/github.com/gyliu513/mcp-go-server/mcp-go-server",
"args": []
}
}
}
Restart Claude Desktop
After you restart Claude Desktop, you will see there is a new tool has been added to Cluade Desktop, and th new tool was shown by a hammer from Claude Desktop.
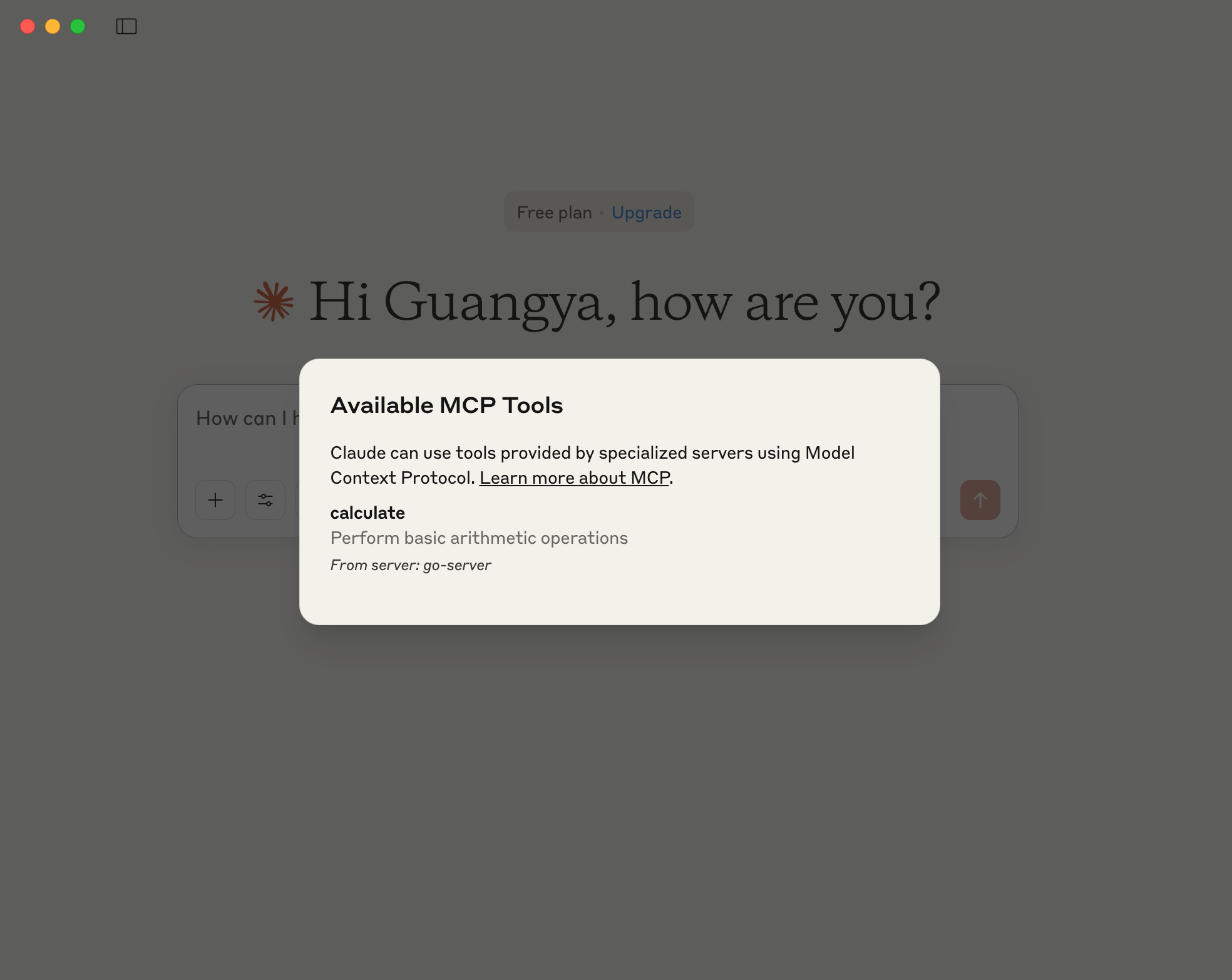
If you click the hammer, you will see the detail of the tool.
OK, you are ready to test this Go MCP Server! Type a query in Claude Desktop and ask What is 4 add 8, the Cluade Desktop will call the Go MCP Server and also pop out window to call the tool.
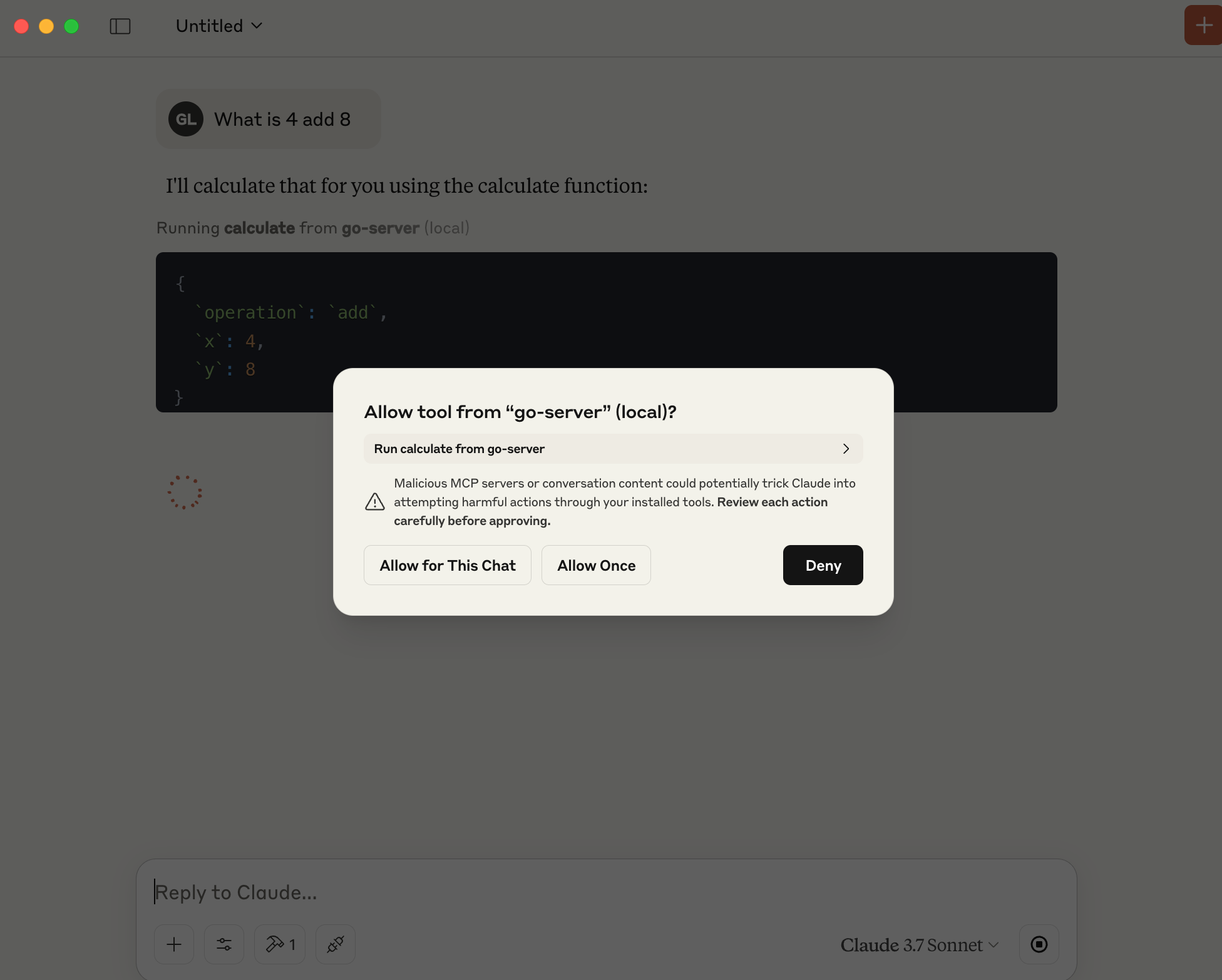
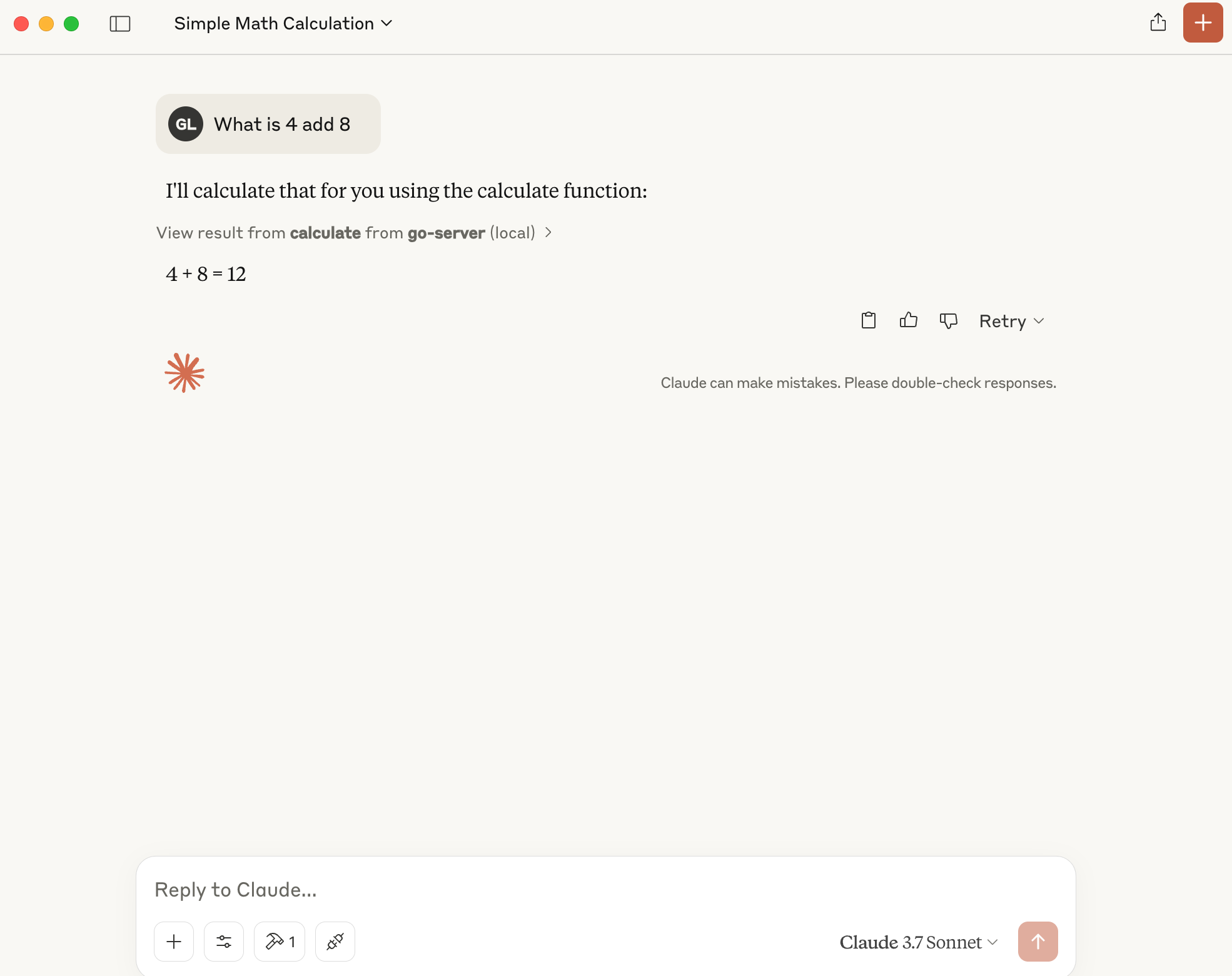
After you click Allow for This Chat, the tool will be called and you will get the answer.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve demonstrated how to rapidly build and run a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server using Go and the mcp-go library. By leveraging Go’s strengths in concurrency, simplicity, and cloud-native readiness, developers can create fast, lightweight, and highly portable MCP servers with minimal effort.
The example calculator tool showcases how easy it is to define, implement, and expose custom tools through MCP, making it ideal for integration with agent frameworks and AI applications like Claude. Whether you’re developing internal utilities, LLM agents, or extending your AI tooling stack, the Go-based MCP server offers a clean and efficient foundation.
As AI applications continue to evolve, having a reliable and performant backend protocol server like this can significantly streamline development and enhance interactivity. With just a few lines of Go code, you’re now equipped to power intelligent agents with real-time computation, customization, and extensibility.
Happy coding — and may your MCP tools be ever productive!